Evaluate a RAG application
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is a technique that enhances Large Language Models (LLMs) by providing them with relevant external knowledge. It has become one of the most widely used approaches for building LLM applications.
This tutorial will show you how to evaluate your RAG applications using LangSmith. You'll learn:
- How to create test datasets
- How to run your RAG application on those datasets
- How to measure your application's performance using different evaluation metrics
Overview
A typical RAG evaluation workflow consists of three main steps:
- Creating a dataset with questions and their expected answers
- Running your RAG application on those questions
- Using evaluators to measure how well your application performed, looking at factors like:
- Answer relevance
- Answer accuracy
- Retrieval quality
For this tutorial, we'll create and evaluate a bot that answers questions about a few of Lilian Weng's insightful blog posts.
Setup
Environment
First, let's set our environment variables:
- Python
- TypeScript
import os
os.environ["LANGSMITH_TRACING"] = "true"
os.environ["LANGSMITH_API_KEY"] = "YOUR LANGSMITH API KEY"
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "YOUR OPENAI API KEY"
process.env.LANGSMITH_TRACING = "true";
process.env.LANGSMITH_API_KEY = "YOUR LANGSMITH API KEY";
process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY = "YOUR OPENAI API KEY";
And install the dependencies we'll need:
- Python
- TypeScript
pip install -U langsmith langchain[openai] langchain-community
yarn add langsmith langchain @langchain/community @langchain/openai
Application
While this tutorial uses LangChain, the evaluation techniques and LangSmith functionality demonstrated here work with any framework. Feel free to use your preferred tools and libraries.
In this section, we'll build a basic Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) application.
We'll stick to a simple implementation that:
- Indexing: chunks and indexes a few of Lilian Weng's blogs in a vector store
- Retrieval: retrieves those chunks based on the user question
- Generation: passes the question and retrieved docs to an LLM.
Indexing and retrieval
First, lets load the blog posts we want to build a chatbot for and index them.
- Python
- TypeScript
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
from langchain_core.vectorstores import InMemoryVectorStore
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
# List of URLs to load documents from
urls = [
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/",
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-03-15-prompt-engineering/",
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-10-25-adv-attack-llm/",
]
# Load documents from the URLs
docs = [WebBaseLoader(url).load() for url in urls]
docs_list = [item for sublist in docs for item in sublist]
# Initialize a text splitter with specified chunk size and overlap
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.from_tiktoken_encoder(
chunk_size=250, chunk_overlap=0
)
# Split the documents into chunks
doc_splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs_list)
# Add the document chunks to the "vector store" using OpenAIEmbeddings
vectorstore = InMemoryVectorStore.from_documents(
documents=doc_splits,
embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings(),
)
# With langchain we can easily turn any vector store into a retrieval component:
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever(k=6)
import { OpenAIEmbeddings } from "@langchain/openai";
import { MemoryVectorStore } from "langchain/vectorstores/memory";
import { BrowserbaseLoader } from "@langchain/community/document_loaders/web/browserbase";
// List of URLs to load documents from
const urls = [
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/",
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-03-15-prompt-engineering/",
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-10-25-adv-attack-llm/",
]
const loader = new BrowserbaseLoader(urls, {
textContent: true,
});
const docs = await loader.load();
const splitter = new RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter({
chunkSize: 1000, chunkOverlap: 200
});
const allSplits = await splitter.splitDocuments(docs);
const embeddings = new OpenAIEmbeddings({
model: "text-embedding-3-large"
});
const vectorStore = new MemoryVectorStore(embeddings);
// Index chunks
await vectorStore.addDocuments(allSplits)
Generation
We can now define the generative pipeline.
- Python
- TypeScript
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langsmith import traceable
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o", temperature=1)
# Add decorator so this function is traced in LangSmith
@traceable()
def rag_bot(question: str) -> dict:
# LangChain retriever will be automatically traced
docs = retriever.invoke(question)
docs_string = "
".join(doc.page_content for doc in docs)
instructions = f"""You are a helpful assistant who is good at analyzing source information and answering questions. Use the following source documents to answer the user's questions. If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know. Use three sentences maximum and keep the answer concise.
Documents:
{docs_string}"""
# langchain ChatModel will be automatically traced
ai_msg = llm.invoke([
{"role": "system", "content": instructions},
{"role": "user", "content": question},
],
)
return {"answer": ai_msg.content, "documents": docs}
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
import { traceable } from "langsmith/traceable";
const llm = new ChatOpenAI({
model: "gpt-4o",
temperature: 1,
})
// Add decorator so this function is traced in LangSmith
const ragBot = traceable(
async (question: string) => {
// LangChain retriever will be automatically traced
const retrievedDocs = await vectorStore.similaritySearch(question);
const docsContent = retrievedDocs.map((doc) => doc.pageContent).join("
");
const instructions = `You are a helpful assistant who is good at analyzing source information and answering questions
Use the following source documents to answer the user's questions.
If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know.
Use three sentences maximum and keep the answer concise.
Documents:
${docsContent}`;
const aiMsg = await llm.invoke([
{
role: "system",
content: instructions
},
{
role: "user",
content: question
}
])
return {"answer": aiMsg.content, "documents": retrievedDocs}
}
)
Dataset
Now that we've got our application, let's build a dataset to evaluate it. Our dataset will be very simple in this case: we'll have example questions and reference answers.
- Python
- TypeScript
from langsmith import Client
client = Client()
# Define the examples for the dataset
examples = [
{
"inputs": {"question": "How does the ReAct agent use self-reflection? "},
"outputs": {"answer": "ReAct integrates reasoning and acting, performing actions - such tools like Wikipedia search API - and then observing / reasoning about the tool outputs."},
},
{
"inputs": {"question": "What are the types of biases that can arise with few-shot prompting?"},
"outputs": {"answer": "The biases that can arise with few-shot prompting include (1) Majority label bias, (2) Recency bias, and (3) Common token bias."},
},
{
"inputs": {"question": "What are five types of adversarial attacks?"},
"outputs": {"answer": "Five types of adversarial attacks are (1) Token manipulation, (2) Gradient based attack, (3) Jailbreak prompting, (4) Human red-teaming, (5) Model red-teaming."},
}
]
# Create the dataset and examples in LangSmith
dataset_name = "Lilian Weng Blogs Q&A"
dataset = client.create_dataset(dataset_name=dataset_name)
client.create_examples(
dataset_id=dataset.id,
examples=examples
)
import { Client } from "langsmith";
const client = new Client();
// Define the examples for the dataset
const examples = [
[
"How does the ReAct agent use self-reflection? ",
"ReAct integrates reasoning and acting, performing actions - such tools like Wikipedia search API - and then observing / reasoning about the tool outputs.",
],
[
"What are the types of biases that can arise with few-shot prompting?",
"The biases that can arise with few-shot prompting include (1) Majority label bias, (2) Recency bias, and (3) Common token bias.",
],
[
"What are five types of adversarial attacks?",
"Five types of adversarial attacks are (1) Token manipulation, (2) Gradient based attack, (3) Jailbreak prompting, (4) Human red-teaming, (5) Model red-teaming.",
]
]
const [inputs, outputs] = examples.reduce<
[Array<{ input: string }>, Array<{ outputs: string }>]
>(
([inputs, outputs], item) => [
[...inputs, { input: item[0] }],
[...outputs, { outputs: item[1] }],
],
[[], []]
);
const datasetName = "Lilian Weng Blogs Q&A";
const dataset = await client.createDataset(datasetName);
await client.createExamples({ inputs, outputs, datasetId: dataset.id })
Evaluators
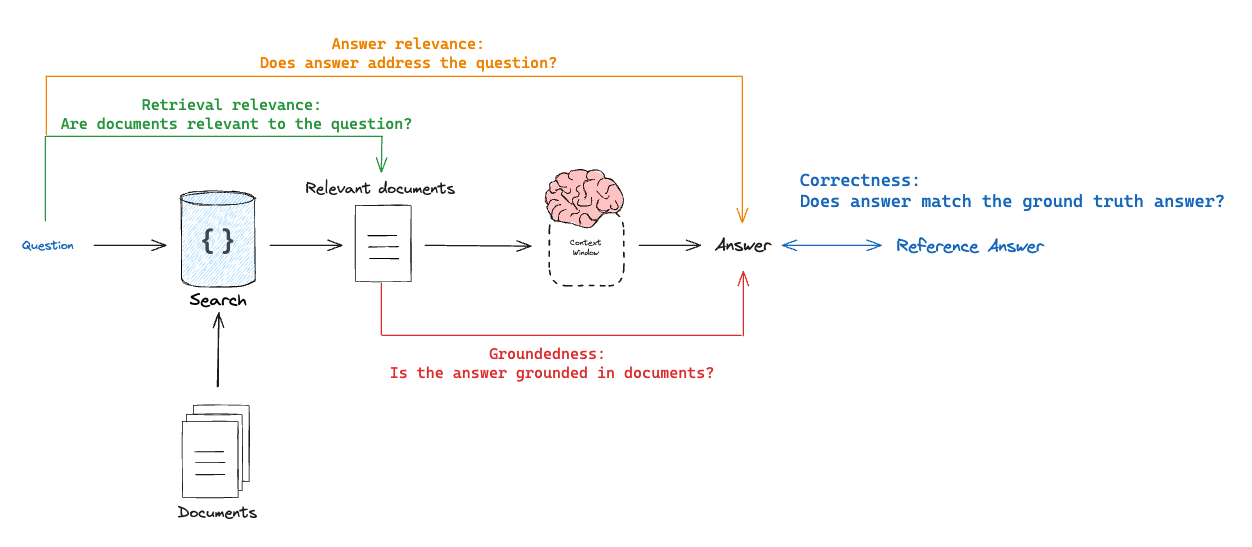
One way to think about different types of RAG evaluators is as a tuple of what is being evaluated X what its being evaluated against:
- Correctness: Response vs reference answer
Goal: Measure "how similar/correct is the RAG chain answer, relative to a ground-truth answer"Mode: Requires a ground truth (reference) answer supplied through a datasetEvaluator: Use LLM-as-judge to assess answer correctness.
- Relevance: Response vs input
Goal: Measure "how well does the generated response address the initial user input"Mode: Does not require reference answer, because it will compare the answer to the input questionEvaluator: Use LLM-as-judge to assess answer relevance, helpfulness, etc.
- Groundedness: Response vs retrieved docs
Goal: Measure "to what extent does the generated response agree with the retrieved context"Mode: Does not require reference answer, because it will compare the answer to the retrieved contextEvaluator: Use LLM-as-judge to assess faithfulness, hallucinations, etc.
- Retrieval relevance: Retrieved docs vs input
Goal: Measure "how relevant are my retrieved results for this query"Mode: Does not require reference answer, because it will compare the question to the retrieved contextEvaluator: Use LLM-as-judge to assess relevance
Correctness: Response vs reference answer
- Python
- TypeScript
from typing_extensions import Annotated, TypedDict
# Grade output schema
class CorrectnessGrade(TypedDict):
# Note that the order in the fields are defined is the order in which the model will generate them.
# It is useful to put explanations before responses because it forces the model to think through
# its final response before generating it:
explanation: Annotated[str, ..., "Explain your reasoning for the score"]
correct: Annotated[bool, ..., "True if the answer is correct, False otherwise."]
# Grade prompt
correctness_instructions = """You are a teacher grading a quiz.
You will be given a QUESTION, the GROUND TRUTH (correct) ANSWER, and the STUDENT ANSWER.
Here is the grade criteria to follow:
(1) Grade the student answers based ONLY on their factual accuracy relative to the ground truth answer.
(2) Ensure that the student answer does not contain any conflicting statements.
(3) It is OK if the student answer contains more information than the ground truth answer, as long as it is factually accurate relative to the ground truth answer.
Correctness:
A correctness value of True means that the student's answer meets all of the criteria.
A correctness value of False means that the student's answer does not meet all of the criteria.
Explain your reasoning in a step-by-step manner to ensure your reasoning and conclusion are correct.
Avoid simply stating the correct answer at the outset."""
# Grader LLM
grader_llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o", temperature=0).with_structured_output(CorrectnessGrade, method="json_schema", strict=True)
def correctness(inputs: dict, outputs: dict, reference_outputs: dict) -> bool:
"""An evaluator for RAG answer accuracy"""
answers = f"""\
QUESTION: {inputs['question']}
GROUND TRUTH ANSWER: {reference_outputs['answer']}
STUDENT ANSWER: {outputs['answer']}"""
# Run evaluator
grade = grader_llm.invoke([
{"role": "system", "content": correctness_instructions},
{"role": "user", "content": answers}
])
return grade["correct"]
import type { EvaluationResult } from "langsmith/evaluation";
import { z } from "zod";
// Grade prompt
const correctnessInstructions = `You are a teacher grading a quiz.
You will be given a QUESTION, the GROUND TRUTH (correct) ANSWER, and the STUDENT ANSWER.
Here is the grade criteria to follow:
(1) Grade the student answers based ONLY on their factual accuracy relative to the ground truth answer.
(2) Ensure that the student answer does not contain any conflicting statements.
(3) It is OK if the student answer contains more information than the ground truth answer, as long as it is factually accurate relative to the ground truth answer.
Correctness:
A correctness value of True means that the student's answer meets all of the criteria.
A correctness value of False means that the student's answer does not meet all of the criteria.
Explain your reasoning in a step-by-step manner to ensure your reasoning and conclusion are correct.
Avoid simply stating the correct answer at the outset.`
const graderLLM = new ChatOpenAI({
model: "gpt-4o",
temperature: 0,
}).withStructuredOutput(
z
.object({
explanation: z
.string()
.describe("Explain your reasoning for the score"),
correct: z
.boolean()
.describe("True if the answer is correct, False otherwise.")
})
.describe("Correctness score for reference answer v.s. generated answer.")
);
async function correctness({
inputs,
outputs,
referenceOutputs,
}: {
inputs: Record<string, any>;
outputs: Record<string, any>;
referenceOutputs?: Record<string, any>;
}): Promise<EvaluationResult> => {
const answer = `QUESTION: ${inputs.question}
GROUND TRUTH ANSWER: ${reference_outputs.answer}
STUDENT ANSWER: ${outputs.answer}`
// Run evaluator
const grade = graderLLM.invoke([{role: "system", content: correctnessInstructions}, {role: "user", content: answer}])
return grade.score
};
Relevance: Response vs input
The flow is similar to above, but we simply look at the inputs and outputs without needing the reference_outputs.
Without a reference answer we can't grade accuracy, but can still grade relevance—as in, did the model address the user's question or not.
- Python
- TypeScript
# Grade output schema
class RelevanceGrade(TypedDict):
explanation: Annotated[str, ..., "Explain your reasoning for the score"]
relevant: Annotated[bool, ..., "Provide the score on whether the answer addresses the question"]
# Grade prompt
relevance_instructions="""You are a teacher grading a quiz.
You will be given a QUESTION and a STUDENT ANSWER.
Here is the grade criteria to follow:
(1) Ensure the STUDENT ANSWER is concise and relevant to the QUESTION
(2) Ensure the STUDENT ANSWER helps to answer the QUESTION
Relevance:
A relevance value of True means that the student's answer meets all of the criteria.
A relevance value of False means that the student's answer does not meet all of the criteria.
Explain your reasoning in a step-by-step manner to ensure your reasoning and conclusion are correct.
Avoid simply stating the correct answer at the outset."""
# Grader LLM
relevance_llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o", temperature=0).with_structured_output(RelevanceGrade, method="json_schema", strict=True)
# Evaluator
def relevance(inputs: dict, outputs: dict) -> bool:
"""A simple evaluator for RAG answer helpfulness."""
answer = f"QUESTION: {inputs['question']}\nSTUDENT ANSWER: {outputs['answer']}"
grade = relevance_llm.invoke([
{"role": "system", "content": relevance_instructions},
{"role": "user", "content": answer}
])
return grade["relevant"]
import type { EvaluationResult } from "langsmith/evaluation";
import { z } from "zod";
// Grade prompt
const relevanceInstructions = `You are a teacher grading a quiz.
You will be given a QUESTION and a STUDENT ANSWER.
Here is the grade criteria to follow:
(1) Ensure the STUDENT ANSWER is concise and relevant to the QUESTION
(2) Ensure the STUDENT ANSWER helps to answer the QUESTION
Relevance:
A relevance value of True means that the student's answer meets all of the criteria.
A relevance value of False means that the student's answer does not meet all of the criteria.
Explain your reasoning in a step-by-step manner to ensure your reasoning and conclusion are correct.
Avoid simply stating the correct answer at the outset.`
const relevanceLLM = new ChatOpenAI({
model: "gpt-4o",
temperature: 0,
}).withStructuredOutput(
z
.object({
explanation: z
.string()
.describe("Explain your reasoning for the score"),
relevant: z
.boolean()
.describe("Provide the score on whether the answer addresses the question")
})
.describe("Relevance score for gene")
);
async function relevance({
inputs,
outputs,
}: {
inputs: Record<string, any>;
outputs: Record<string, any>;
}): Promise<EvaluationResult> => {
const answer = `QUESTION: ${inputs.question}
STUDENT ANSWER: ${outputs.answer}`
// Run evaluator
const grade = relevanceLLM.invoke([{role: "system", content: relevanceInstructions}, {role: "user", content: answer}])
return grade.relevant
};
Groundedness: Response vs retrieved docs
Another useful way to evaluate responses without needing reference answers is to check if the response is justified by (or "grounded in") the retrieved documents.
- Python
- TypeScript
# Grade output schema
class GroundedGrade(TypedDict):
explanation: Annotated[str, ..., "Explain your reasoning for the score"]
grounded: Annotated[bool, ..., "Provide the score on if the answer hallucinates from the documents"]
# Grade prompt
grounded_instructions = """You are a teacher grading a quiz.
You will be given FACTS and a STUDENT ANSWER.
Here is the grade criteria to follow:
(1) Ensure the STUDENT ANSWER is grounded in the FACTS.
(2) Ensure the STUDENT ANSWER does not contain "hallucinated" information outside the scope of the FACTS.
Grounded:
A grounded value of True means that the student's answer meets all of the criteria.
A grounded value of False means that the student's answer does not meet all of the criteria.
Explain your reasoning in a step-by-step manner to ensure your reasoning and conclusion are correct.
Avoid simply stating the correct answer at the outset."""
# Grader LLM
grounded_llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o", temperature=0).with_structured_output(GroundedGrade, method="json_schema", strict=True)
# Evaluator
def groundedness(inputs: dict, outputs: dict) -> bool:
"""A simple evaluator for RAG answer groundedness."""
doc_string = "\n\n".join(doc.page_content for doc in outputs["documents"])
answer = f"FACTS: {doc_string}\nSTUDENT ANSWER: {outputs['answer']}"
grade = grounded_llm.invoke([{"role": "system", "content": grounded_instructions}, {"role": "user", "content": answer}])
return grade["grounded"]
import type { EvaluationResult } from "langsmith/evaluation";
import { z } from "zod";
// Grade prompt
const groundedInstructions = `You are a teacher grading a quiz.
You will be given FACTS and a STUDENT ANSWER.
Here is the grade criteria to follow:
(1) Ensure the STUDENT ANSWER is grounded in the FACTS.
(2) Ensure the STUDENT ANSWER does not contain "hallucinated" information outside the scope of the FACTS.
Grounded:
A grounded value of True means that the student's answer meets all of the criteria.
A grounded value of False means that the student's answer does not meet all of the criteria.
Explain your reasoning in a step-by-step manner to ensure your reasoning and conclusion are correct.
Avoid simply stating the correct answer at the outset.`
const groundedLLM = new ChatOpenAI({
model: "gpt-4o",
temperature: 0,
}).withStructuredOutput(
z
.object({
explanation: z
.string()
.describe("Explain your reasoning for the score"),
grounded: z
.boolean()
.describe("Provide the score on if the answer hallucinates from the documents")
})
.describe("Grounded score for the answer from the retrieved documents.")
);
async function grounded({
inputs,
outputs,
}: {
inputs: Record<string, any>;
outputs: Record<string, any>;
}): Promise<EvaluationResult> => {
const docString = outputs.documents.map((doc) => doc.pageContent).join("
");
const answer = `FACTS: ${docString}
STUDENT ANSWER: ${outputs.answer}`
// Run evaluator
const grade = groundedLLM.invoke([{role: "system", content: groundedInstructions}, {role: "user", content: answer}])
return grade.grounded
};
Retrieval relevance: Retrieved docs vs input
- Python
- TypeScript
# Grade output schema
class RetrievalRelevanceGrade(TypedDict):
explanation: Annotated[str, ..., "Explain your reasoning for the score"]
relevant: Annotated[bool, ..., "True if the retrieved documents are relevant to the question, False otherwise"]
# Grade prompt
retrieval_relevance_instructions = """You are a teacher grading a quiz.
You will be given a QUESTION and a set of FACTS provided by the student.
Here is the grade criteria to follow:
(1) You goal is to identify FACTS that are completely unrelated to the QUESTION
(2) If the facts contain ANY keywords or semantic meaning related to the question, consider them relevant
(3) It is OK if the facts have SOME information that is unrelated to the question as long as (2) is met
Relevance:
A relevance value of True means that the FACTS contain ANY keywords or semantic meaning related to the QUESTION and are therefore relevant.
A relevance value of False means that the FACTS are completely unrelated to the QUESTION.
Explain your reasoning in a step-by-step manner to ensure your reasoning and conclusion are correct.
Avoid simply stating the correct answer at the outset."""
# Grader LLM
retrieval_relevance_llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o", temperature=0).with_structured_output(RetrievalRelevanceGrade, method="json_schema", strict=True)
def retrieval_relevance(inputs: dict, outputs: dict) -> bool:
"""An evaluator for document relevance"""
doc_string = "\n\n".join(doc.page_content for doc in outputs["documents"])
answer = f"FACTS: {doc_string}\nQUESTION: {inputs['question']}"
# Run evaluator
grade = retrieval_relevance_llm.invoke([
{"role": "system", "content": retrieval_relevance_instructions},
{"role": "user", "content": answer}
])
return grade["relevant"]
import type { EvaluationResult } from "langsmith/evaluation";
import { z } from "zod";
// Grade prompt
const retrievalRelevanceInstructions = `You are a teacher grading a quiz.
You will be given a QUESTION and a set of FACTS provided by the student.
Here is the grade criteria to follow:
(1) You goal is to identify FACTS that are completely unrelated to the QUESTION
(2) If the facts contain ANY keywords or semantic meaning related to the question, consider them relevant
(3) It is OK if the facts have SOME information that is unrelated to the question as long as (2) is met
Relevance:
A relevance value of True means that the FACTS contain ANY keywords or semantic meaning related to the QUESTION and are therefore relevant.
A relevance value of False means that the FACTS are completely unrelated to the QUESTION.
Explain your reasoning in a step-by-step manner to ensure your reasoning and conclusion are correct.
Avoid simply stating the correct answer at the outset.`
const retrievalRelevanceLLM = new ChatOpenAI({
model: "gpt-4o",
temperature: 0,
}).withStructuredOutput(
z
.object({
explanation: z
.string()
.describe("Explain your reasoning for the score"),
relevant: z
.boolean()
.describe("True if the retrieved documents are relevant to the question, False otherwise")
})
.describe("Retrieval relevance score for the retrieved documents v.s. the question.")
);
async function retrievalRelevance({
inputs,
outputs,
}: {
inputs: Record<string, any>;
outputs: Record<string, any>;
}): Promise<EvaluationResult> => {
const docString = outputs.documents.map((doc) => doc.pageContent).join("
");
const answer = `FACTS: ${docString}
QUESTION: ${inputs.question}`
// Run evaluator
const grade = retrievalRelevanceLLM.invoke([{role: "system", content: retrievalRelevanceInstructions}, {role: "user", content: answer}])
return grade.relevant
};
Run evaluation
We can now kick off our evaluation job with all of our different evaluators.
- Python
- TypeScript
def target(inputs: dict) -> dict:
return rag_bot(inputs["question"])
experiment_results = client.evaluate(
target,
data=dataset_name,
evaluators=[correctness, groundedness, relevance, retrieval_relevance],
experiment_prefix="rag-doc-relevance",
metadata={"version": "LCEL context, gpt-4-0125-preview"},
)
# Explore results locally as a dataframe if you have pandas installed
# experiment_results.to_pandas()
import { evaluate } from "langsmith/evaluation";
const targetFunc = (inputs: Record<string, any>) => {
return ragBot(inputs.question)
};
const experimentResults = await evaluate(targetFunc, {
data: datasetName,
evaluators: [correctness, groundedness, relevance, retrievalRelevance],
experimentPrefix="rag-doc-relevance",
metadata={version: "LCEL context, gpt-4-0125-preview"},
});
You can see an example of what these results look like here: LangSmith link
Reference code
Here's a consolidated script with all the above code:
- Python
- TypeScript
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
from langchain_core.vectorstores import InMemoryVectorStore
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI, OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langsmith import Client, traceable
from typing_extensions import Annotated, TypedDict
# List of URLs to load documents from
urls = [
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/",
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-03-15-prompt-engineering/",
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-10-25-adv-attack-llm/",
]
# Load documents from the URLs
docs = [WebBaseLoader(url).load() for url in urls]
docs_list = [item for sublist in docs for item in sublist]
# Initialize a text splitter with specified chunk size and overlap
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.from_tiktoken_encoder(
chunk_size=250, chunk_overlap=0
)
# Split the documents into chunks
doc_splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs_list)
# Add the document chunks to the "vector store" using OpenAIEmbeddings
vectorstore = InMemoryVectorStore.from_documents(
documents=doc_splits,
embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings(),
)
# With langchain we can easily turn any vector store into a retrieval component:
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever(k=6)
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o", temperature=1)
# Add decorator so this function is traced in LangSmith
@traceable()
def rag_bot(question: str) -> dict:
# langchain Retriever will be automatically traced
docs = retriever.invoke(question)
docs_string = "
".join(doc.page_content for doc in docs)
instructions = f"""You are a helpful assistant who is good at analyzing source information and answering questions. Use the following source documents to answer the user's questions. If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know. Use three sentences maximum and keep the answer concise.
Documents:
{docs_string}"""
# langchain ChatModel will be automatically traced
ai_msg = llm.invoke(
[
{"role": "system", "content": instructions},
{"role": "user", "content": question},
],
)
return {"answer": ai_msg.content, "documents": docs}
client = Client()
# Define the examples for the dataset
examples = [
{
"inputs": {"question": "How does the ReAct agent use self-reflection? "},
"outputs": {"answer": "ReAct integrates reasoning and acting, performing actions - such tools like Wikipedia search API - and then observing / reasoning about the tool outputs."},
},
{
"inputs": {"question": "What are the types of biases that can arise with few-shot prompting?"},
"outputs": {"answer": "The biases that can arise with few-shot prompting include (1) Majority label bias, (2) Recency bias, and (3) Common token bias."},
},
{
"inputs": {"question": "What are five types of adversarial attacks?"},
"outputs": {"answer": "Five types of adversarial attacks are (1) Token manipulation, (2) Gradient based attack, (3) Jailbreak prompting, (4) Human red-teaming, (5) Model red-teaming."},
},
]
# Create the dataset and examples in LangSmith
dataset_name = "Lilian Weng Blogs Q&A"
if not client.has_dataset(dataset_name=dataset_name):
dataset = client.create_dataset(dataset_name=dataset_name)
client.create_examples(
dataset_id=dataset.id,
examples=examples
)
# Grade output schema
class CorrectnessGrade(TypedDict):
# Note that the order in the fields are defined is the order in which the model will generate them.
# It is useful to put explanations before responses because it forces the model to think through
# its final response before generating it:
explanation: Annotated[str, ..., "Explain your reasoning for the score"]
correct: Annotated[bool, ..., "True if the answer is correct, False otherwise."]
# Grade prompt
correctness_instructions = """You are a teacher grading a quiz.
You will be given a QUESTION, the GROUND TRUTH (correct) ANSWER, and the STUDENT ANSWER.
Here is the grade criteria to follow:
(1) Grade the student answers based ONLY on their factual accuracy relative to the ground truth answer.
(2) Ensure that the student answer does not contain any conflicting statements.
(3) It is OK if the student answer contains more information than the ground truth answer, as long as it is factually accurate relative to the ground truth answer.
Correctness:
A correctness value of True means that the student's answer meets all of the criteria.
A correctness value of False means that the student's answer does not meet all of the criteria.
Explain your reasoning in a step-by-step manner to ensure your reasoning and conclusion are correct.
Avoid simply stating the correct answer at the outset."""
# Grader LLM
grader_llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o", temperature=0).with_structured_output(
CorrectnessGrade, method="json_schema", strict=True
)
def correctness(inputs: dict, outputs: dict, reference_outputs: dict) -> bool:
"""An evaluator for RAG answer accuracy"""
answers = f"""\
QUESTION: {inputs['question']}
GROUND TRUTH ANSWER: {reference_outputs['answer']}
STUDENT ANSWER: {outputs['answer']}"""
# Run evaluator
grade = grader_llm.invoke(
[
{"role": "system", "content": correctness_instructions},
{"role": "user", "content": answers},
]
)
return grade["correct"]
# Grade output schema
class RelevanceGrade(TypedDict):
explanation: Annotated[str, ..., "Explain your reasoning for the score"]
relevant: Annotated[
bool, ..., "Provide the score on whether the answer addresses the question"
]
# Grade prompt
relevance_instructions = """You are a teacher grading a quiz.
You will be given a QUESTION and a STUDENT ANSWER.
Here is the grade criteria to follow:
(1) Ensure the STUDENT ANSWER is concise and relevant to the QUESTION
(2) Ensure the STUDENT ANSWER helps to answer the QUESTION
Relevance:
A relevance value of True means that the student's answer meets all of the criteria.
A relevance value of False means that the student's answer does not meet all of the criteria.
Explain your reasoning in a step-by-step manner to ensure your reasoning and conclusion are correct.
Avoid simply stating the correct answer at the outset."""
# Grader LLM
relevance_llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o", temperature=0).with_structured_output(
RelevanceGrade, method="json_schema", strict=True
)
# Evaluator
def relevance(inputs: dict, outputs: dict) -> bool:
"""A simple evaluator for RAG answer helpfulness."""
answer = f"QUESTION: {inputs['question']}\nSTUDENT ANSWER: {outputs['answer']}"
grade = relevance_llm.invoke(
[
{"role": "system", "content": relevance_instructions},
{"role": "user", "content": answer},
]
)
return grade["relevant"]
# Grade output schema
class GroundedGrade(TypedDict):
explanation: Annotated[str, ..., "Explain your reasoning for the score"]
grounded: Annotated[
bool, ..., "Provide the score on if the answer hallucinates from the documents"
]
# Grade prompt
grounded_instructions = """You are a teacher grading a quiz.
You will be given FACTS and a STUDENT ANSWER.
Here is the grade criteria to follow:
(1) Ensure the STUDENT ANSWER is grounded in the FACTS.
(2) Ensure the STUDENT ANSWER does not contain "hallucinated" information outside the scope of the FACTS.
Grounded:
A grounded value of True means that the student's answer meets all of the criteria.
A grounded value of False means that the student's answer does not meet all of the criteria.
Explain your reasoning in a step-by-step manner to ensure your reasoning and conclusion are correct.
Avoid simply stating the correct answer at the outset."""
# Grader LLM
grounded_llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o", temperature=0).with_structured_output(
GroundedGrade, method="json_schema", strict=True
)
# Evaluator
def groundedness(inputs: dict, outputs: dict) -> bool:
"""A simple evaluator for RAG answer groundedness."""
doc_string = "\n\n".join(doc.page_content for doc in outputs["documents"])
answer = f"FACTS: {doc_string}\nSTUDENT ANSWER: {outputs['answer']}"
grade = grounded_llm.invoke(
[
{"role": "system", "content": grounded_instructions},
{"role": "user", "content": answer},
]
)
return grade["grounded"]
# Grade output schema
class RetrievalRelevanceGrade(TypedDict):
explanation: Annotated[str, ..., "Explain your reasoning for the score"]
relevant: Annotated[
bool,
...,
"True if the retrieved documents are relevant to the question, False otherwise",
]
# Grade prompt
retrieval_relevance_instructions = """You are a teacher grading a quiz.
You will be given a QUESTION and a set of FACTS provided by the student.
Here is the grade criteria to follow:
(1) You goal is to identify FACTS that are completely unrelated to the QUESTION
(2) If the facts contain ANY keywords or semantic meaning related to the question, consider them relevant
(3) It is OK if the facts have SOME information that is unrelated to the question as long as (2) is met
Relevance:
A relevance value of True means that the FACTS contain ANY keywords or semantic meaning related to the QUESTION and are therefore relevant.
A relevance value of False means that the FACTS are completely unrelated to the QUESTION.
Explain your reasoning in a step-by-step manner to ensure your reasoning and conclusion are correct.
Avoid simply stating the correct answer at the outset."""
# Grader LLM
retrieval_relevance_llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-4o", temperature=0
).with_structured_output(RetrievalRelevanceGrade, method="json_schema", strict=True)
def retrieval_relevance(inputs: dict, outputs: dict) -> bool:
"""An evaluator for document relevance"""
doc_string = "\n\n".join(doc.page_content for doc in outputs["documents"])
answer = f"FACTS: {doc_string}\nQUESTION: {inputs['question']}"
# Run evaluator
grade = retrieval_relevance_llm.invoke(
[
{"role": "system", "content": retrieval_relevance_instructions},
{"role": "user", "content": answer},
]
)
return grade["relevant"]
def target(inputs: dict) -> dict:
return rag_bot(inputs["question"])
experiment_results = client.evaluate(
target,
data=dataset_name,
evaluators=[correctness, groundedness, relevance, retrieval_relevance],
experiment_prefix="rag-doc-relevance",
metadata={"version": "LCEL context, gpt-4-0125-preview"},
)
# Explore results locally as a dataframe if you have pandas installed
# experiment_results.to_pandas()
import { OpenAIEmbeddings, ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
import { MemoryVectorStore } from "langchain/vectorstores/memory";
import { BrowserbaseLoader } from "@langchain/community/document_loaders/web/browserbase";
import { traceable } from "langsmith/traceable";
import { Client } from "langsmith";
import { evaluate, type EvaluationResult } from "langsmith/evaluation";
import { z } from "zod";
// List of URLs to load documents from
const urls = [
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/",
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-03-15-prompt-engineering/",
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-10-25-adv-attack-llm/",
]
const loader = new BrowserbaseLoader(urls, {
textContent: true,
});
const docs = await loader.load();
const splitter = new RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter({
chunkSize: 1000, chunkOverlap: 200
});
const allSplits = await splitter.splitDocuments(docs);
const embeddings = new OpenAIEmbeddings({
model: "text-embedding-3-large"
});
const vectorStore = new MemoryVectorStore(embeddings);
// Index chunks
await vectorStore.addDocuments(allSplits)
const llm = new ChatOpenAI({
model: "gpt-4o",
temperature: 1,
})
// Add decorator so this function is traced in LangSmith
const ragBot = traceable(
async (question: string) => {
// LangChain retriever will be automatically traced
const retrievedDocs = await vectorStore.similaritySearch(question);
const docsContent = retrievedDocs.map((doc) => doc.pageContent).join("
");
const instructions = `You are a helpful assistant who is good at analyzing source information and answering questions.
Use the following source documents to answer the user's questions.
If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know.
Use three sentences maximum and keep the answer concise.
Documents:
${docsContent}`
const aiMsg = await llm.invoke([
{
role: "system",
content: instructions
},
{
role: "user",
content: question
}
])
return {"answer": aiMsg.content, "documents": retrievedDocs}
}
)
const client = new Client();
// Define the examples for the dataset
const examples = [
[
"How does the ReAct agent use self-reflection? ",
"ReAct integrates reasoning and acting, performing actions - such tools like Wikipedia search API - and then observing / reasoning about the tool outputs.",
],
[
"What are the types of biases that can arise with few-shot prompting?",
"The biases that can arise with few-shot prompting include (1) Majority label bias, (2) Recency bias, and (3) Common token bias.",
],
[
"What are five types of adversarial attacks?",
"Five types of adversarial attacks are (1) Token manipulation, (2) Gradient based attack, (3) Jailbreak prompting, (4) Human red-teaming, (5) Model red-teaming.",
]
]
const [inputs, outputs] = examples.reduce<
[Array<{ input: string }>, Array<{ outputs: string }>]
>(
([inputs, outputs], item) => [
[...inputs, { input: item[0] }],
[...outputs, { outputs: item[1] }],
],
[[], []]
);
const datasetName = "Lilian Weng Blogs Q&A";
const dataset = await client.createDataset(datasetName);
await client.createExamples({ inputs, outputs, datasetId: dataset.id })
// Grade prompt
const correctnessInstructions = `You are a teacher grading a quiz.
You will be given a QUESTION, the GROUND TRUTH (correct) ANSWER, and the STUDENT ANSWER.
Here is the grade criteria to follow:
(1) Grade the student answers based ONLY on their factual accuracy relative to the ground truth answer.
(2) Ensure that the student answer does not contain any conflicting statements.
(3) It is OK if the student answer contains more information than the ground truth answer, as long as it is factually accurate relative to the ground truth answer.
Correctness:
A correctness value of True means that the student's answer meets all of the criteria.
A correctness value of False means that the student's answer does not meet all of the criteria.
Explain your reasoning in a step-by-step manner to ensure your reasoning and conclusion are correct.
Avoid simply stating the correct answer at the outset.`
const graderLLM = new ChatOpenAI({
model: "gpt-4o",
temperature: 0,
}).withStructuredOutput(
z
.object({
explanation: z
.string()
.describe("Explain your reasoning for the score"),
correct: z
.boolean()
.describe("True if the answer is correct, False otherwise.")
})
.describe("Correctness score for reference answer v.s. generated answer.")
);
async function correctness({
inputs,
outputs,
referenceOutputs,
}: {
inputs: Record<string, any>;
outputs: Record<string, any>;
referenceOutputs?: Record<string, any>;
}): Promise<EvaluationResult> => {
const answer = `QUESTION: ${inputs.question}
GROUND TRUTH ANSWER: ${reference_outputs.answer}
STUDENT ANSWER: ${outputs.answer}`
// Run evaluator
const grade = graderLLM.invoke([{role: "system", content: correctnessInstructions}, {role: "user", content: answer}])
return grade.score
};
// Grade prompt
const relevanceInstructions = `You are a teacher grading a quiz.
You will be given a QUESTION and a STUDENT ANSWER.
Here is the grade criteria to follow:
(1) Ensure the STUDENT ANSWER is concise and relevant to the QUESTION
(2) Ensure the STUDENT ANSWER helps to answer the QUESTION
Relevance:
A relevance value of True means that the student's answer meets all of the criteria.
A relevance value of False means that the student's answer does not meet all of the criteria.
Explain your reasoning in a step-by-step manner to ensure your reasoning and conclusion are correct.
Avoid simply stating the correct answer at the outset.`
const relevanceLLM = new ChatOpenAI({
model: "gpt-4o",
temperature: 0,
}).withStructuredOutput(
z
.object({
explanation: z
.string()
.describe("Explain your reasoning for the score"),
relevant: z
.boolean()
.describe("Provide the score on whether the answer addresses the question")
})
.describe("Relevance score for gene")
);
async function relevance({
inputs,
outputs,
}: {
inputs: Record<string, any>;
outputs: Record<string, any>;
}): Promise<EvaluationResult> => {
const answer = `QUESTION: ${inputs.question}
STUDENT ANSWER: ${outputs.answer}`
// Run evaluator
const grade = relevanceLLM.invoke([{role: "system", content: relevanceInstructions}, {role: "user", content: answer}])
return grade.relevant
};
// Grade prompt
const groundedInstructions = `You are a teacher grading a quiz.
You will be given FACTS and a STUDENT ANSWER.
Here is the grade criteria to follow:
(1) Ensure the STUDENT ANSWER is grounded in the FACTS.
(2) Ensure the STUDENT ANSWER does not contain "hallucinated" information outside the scope of the FACTS.
Grounded:
A grounded value of True means that the student's answer meets all of the criteria.
A grounded value of False means that the student's answer does not meet all of the criteria.
Explain your reasoning in a step-by-step manner to ensure your reasoning and conclusion are correct.
Avoid simply stating the correct answer at the outset.`
const groundedLLM = new ChatOpenAI({
model: "gpt-4o",
temperature: 0,
}).withStructuredOutput(
z
.object({
explanation: z
.string()
.describe("Explain your reasoning for the score"),
grounded: z
.boolean()
.describe("Provide the score on if the answer hallucinates from the documents")
})
.describe("Grounded score for the answer from the retrieved documents.")
);
async function grounded({
inputs,
outputs,
}: {
inputs: Record<string, any>;
outputs: Record<string, any>;
}): Promise<EvaluationResult> => {
const docString = outputs.documents.map((doc) => doc.pageContent).join("
");
const answer = `FACTS: ${docString}
STUDENT ANSWER: ${outputs.answer}`
// Run evaluator
const grade = groundedLLM.invoke([{role: "system", content: groundedInstructions}, {role: "user", content: answer}])
return grade.grounded
};
// Grade prompt
const retrievalRelevanceInstructions = `You are a teacher grading a quiz.
You will be given a QUESTION and a set of FACTS provided by the student.
Here is the grade criteria to follow:
(1) You goal is to identify FACTS that are completely unrelated to the QUESTION
(2) If the facts contain ANY keywords or semantic meaning related to the question, consider them relevant
(3) It is OK if the facts have SOME information that is unrelated to the question as long as (2) is met
Relevance:
A relevance value of True means that the FACTS contain ANY keywords or semantic meaning related to the QUESTION and are therefore relevant.
A relevance value of False means that the FACTS are completely unrelated to the QUESTION.
Explain your reasoning in a step-by-step manner to ensure your reasoning and conclusion are correct.
Avoid simply stating the correct answer at the outset.`
const retrievalRelevanceLLM = new ChatOpenAI({
model: "gpt-4o",
temperature: 0,
}).withStructuredOutput(
z
.object({
explanation: z
.string()
.describe("Explain your reasoning for the score"),
relevant: z
.boolean()
.describe("True if the retrieved documents are relevant to the question, False otherwise")
})
.describe("Retrieval relevance score for the retrieved documents v.s. the question.")
);
async function retrievalRelevance({
inputs,
outputs,
}: {
inputs: Record<string, any>;
outputs: Record<string, any>;
}): Promise<EvaluationResult> => {
const docString = outputs.documents.map((doc) => doc.pageContent).join("
");
const answer = `FACTS: ${docString}
QUESTION: ${inputs.question}`
// Run evaluator
const grade = retrievalRelevanceLLM.invoke([{role: "system", content: retrievalRelevanceInstructions}, {role: "user", content: answer}])
return grade.relevant
};
const targetFunc = (input: Record<string, any>) => {
return ragBot(inputs.question)
};
const experimentResults = await evaluate(targetFunc, {
data: datasetName,
evaluators: [correctness, groundedness, relevance, retrievalRelevance],
experimentPrefix="rag-doc-relevance",
metadata={version: "LCEL context, gpt-4-0125-preview"},
});